All About Smartphone's Fingerprint Scanners
In recent few years, fingerprint scanners in smartphones become very common. Not only flagship phones but even budget smartphones are now equipped fingerprint scanners. Nowadays, fingerprint scanners took their place in the display of some flagship smartphones. Yes, we’re talking about In-Display fingerprint scanners, embedded in few phones such as Vivo X20 Plus, Vivo X21, Vivo V11 Pro, Xiomi Mi 8 and few more. While In-display fingerprint scanners haven’t properly made their place in the market, engineers are researching & developing Ultrasonic In-Display fingerprint scanners.
We are pretty sure that you’ve used fingerprint scanner in your life at least at once to unlock any device. But have you ever wonder how these fingerprint scanners work? We are going to cover all about them in this article.
How Does A Fingerprint Scanner Works?
As you know, every person on this planet has their unique fingerprints. Thus it creates a better security key for an individual. What a fingerprint scanner does is it takes an image of the fingerprint which is known as live-scan, then it creates a pattern of ridges and valleys in this image and saves it as a biometric template in the smartphone’s database. This biometric template is later used to match and unlock the device.
OPTICAL FINGERPRINT SCANNERS

These are the oldest one in the market for fingerprint scanning, you must have seen these at the Adhaar Card Kendra, SIM distributors and in offices for attendance and now in some smartphones too. You have just read above how fingerprint scanners work. Optical follows the same procedure mentioned above but in its own way of capturing images like a camera. A light is projected on the finger using LEDs and then the sensors which will be CCD or CMOS captures the reflected light and creates a grayscale image of the fingerprint. The image is then studied where darker areas are represented as more reflected light and light areas as less reflected light. Actually, darker areas are the ridges while lighted areas are the valleys of the fingerprint. If you’ve seen in movies, hackers take an impression of the fingerprint on tape and breach the security of the optical scanners. Similarly, they are very weak at this point in real life too. But nowadays, they’ve made their comeback as In-Display Fingerprint Scanners embedded just beneath the screens of the smartphones like Vivo V11 Pro. These ones are more reliable than their older versions but still slow as compare to capacitive scanners.
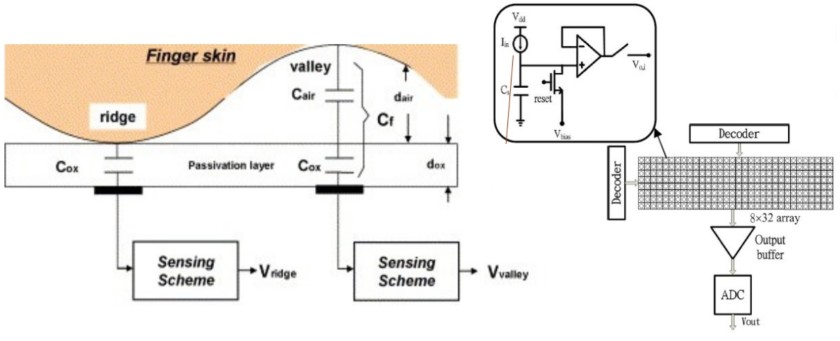
CAPACITIVE TOUCHSCANNER
This scanner is the most common fingerprint scanner on smartphones nowadays, maybe your phone also has this one. As the name suggests, capacitive, the core part of this scanner is capacitors.
This scanner has arrays (collections) of tiny capacitor circuit with collect the data and makes the pattern. If you’re familiar with capacitors you must know that capacitors store energy. When you place your finger on the plate of the scanner then where the ridges touch the plate those capacitors underneath the ridges get charged while rest of the capacitors stay uncharged as valleys of the finger falls there. Thus, using an operational-amplifier IC the changes are being tracked and a pattern is registered in the memory for future use.
The advantage of this design is that it is impossible to fool as compared to optical scanners. But can be hacked using hardware or software hacking.
ULTRASONIC SCANNERS
The latest and could be the most secure fingerprint scanner technology for smartphones. This technology has made its debut in Le Max Pro featuring
Sense ID, another piece of Qualcomm technology. Apparently, there is no other commercial phone available in the market with an ultrasonic scanner.
Sense ID, another piece of Qualcomm technology. Apparently, there is no other commercial phone available in the market with an ultrasonic scanner.
As its name suggests Ultrasonic, it has an ultrasonic transmitter and a receiver. An ultrasonic pulse is transmitted against the finger when the finger is placed on the scanner plate. Then some of the pulses are absorbed by the finger and some bounce back to the receiver which collects the pulses and calculates the intensity of the returning pulses from different places of the scanner plate. Using this method, the chip creates a high-quality 3D image of the image of the scanned finger and this 3D image is later used for unlocking the device.
This technology is highly secure than capacitive scanners and optical scanners. And could be a better alternative for those whether the manufacturer places it beneath the display or dedicate a plate-like place for the scanner. Apparently, this technology would take about 2- 3 years to arrive for commercial phones. At MWC 2017, Vivo had announced its concept smartphone equipped ultrasonic scanner, though it was not as accurate as capacitive which indicates that it needs much more research and development.
CONCLUSION
These days everybody is looking for a fingerprint scanner while buying new smartphones, and they’re now equipped in budget phones too. Optical scanners are still limited to flagship phones, and ultrasonic is yet to arrive. However, fingerprint scanners are now an integral part in smartphones and they’re making unlocking device time minimum without compromising the security.
All About Smartphone's Fingerprint Scanners
![All About Smartphone's Fingerprint Scanners]() Reviewed by Dazzler Kumar
on
February 19, 2019
Rating:
Reviewed by Dazzler Kumar
on
February 19, 2019
Rating:






No comments